Realize your dreams with our affordable loans.
Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
PMEGP SCHEME LOAN
INTRODUCTION
PMEGP is a central sector scheme administered by the ministry of micro,small and medium enterprises (MoMSME).The scheme is implemented by khadi and village industries commission (KVIC) functioning as the nodal agency at the national level.At the state level ,the scheme is implemented through state KVIC directoates,state khadi and village Industries boards (KVIBs),District Industries centers (DICs),and coi board ,known as the Implementing Agencies.
- ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
- To generate employment opportunities in rural as well as urban areas of the country through setting up of new self – employment ventures/projects / micro enterprises.
- To bring together widely dispersed traditional artisans /rural and urban unemployed youth and given them self – employment opportunities to the extent possible ,at their place .
- To provide continuous and sustainable employment to a large segment of traditional and prospective artisans and rural and urban unemployed youth in the country , so as to help arrest migration of rural youth to urban area.
- To increase the wage – earning capacity of artisans and contribute to increase in the growth rate of rural and urban employment.

OBJECTIVES
To provide continuous and sustainable employment to a large segment of traditional and prospective artisans, rural and urban unemployed youth in the country through setting up of micro enterprises. To facilitate participation of financial institutions for higher credit flow to micro sector.
PMFME LOAN
INTRODUCTION
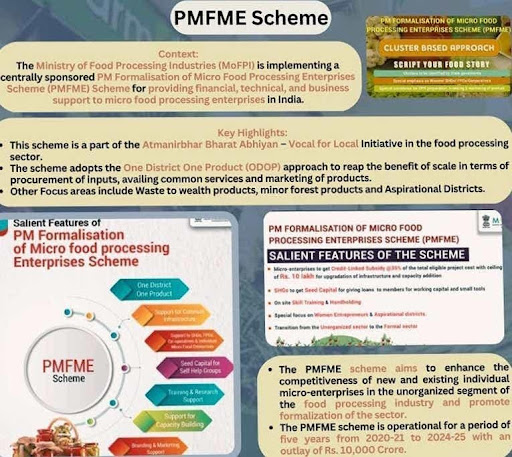
Ministry of Food Processing Industry (MoFPI) has launched the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan with the aim to enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganized segment of the food processing ..
- OBJECTIVES
- Increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, FPOs, Self Help Groups and Co-operatives.
- Integration with organized supply chain by strengthening branding & marketing.
- Support for transition of existing 2,00,000 enterprises into formal framework.
- Increased access to common services like common processing facility, laboratories, storage, packaging, marketing and incubation services.
- Strengthening of institutions, research and training in the food processing sector andtion services.
- lncreased access for the enterprises, to professional and technical support.

UYEGP SHEME
INTRODUCTION
The Government of Tamil Nadu, Department of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, has launched the Unemployed Youth Employment Generation Programme (UYEGP). In addition to overcoming several other business hurdles, an entrepreneur must get urgent financing to launch a new firm. There are or might be circumstances in which banks won’t help them for the first time, whatever the reasons may be. The government of Tamil Nadu has implemented a credit program for small enterprises in order to remedy this issue. UYEGP Scheme is a program designed to inspire unemployed young people to create their own companies and foster youth entrepreneurship.The state government has taken up concerns to help, but in order to achieve their aim, they have put down some constraints as well, such as age, educational qualifications, and family income, that must be met before applying under the scheme. This program will only make loans up to 90-95% of the project’s cost, with a 25% subsidy available to eligible beneficiaries. The good news is that no assets or guarantees are needed from the applicant. Support with loans through commercial banks will be given. Overall, promoters’ contributions will be no more than 10% of the given scheme, and the rest of the parties involved in the scheme will help newbies to start a business.
OBJECTIVES
The primary objective of this UYEGP scheme is to reduce unemployment among socially and economically disadvantaged sections of the population, particularly among the educated and unemployed, by enabling them to become self-employed by establishing service, manufacturing, and business enterprises with the aid of a loan and subsidy from the state government. Serving all poor sections of the state means the government is trying to make a better life for citizens of minority groups.
ANNAL AMBEDKAR BUSINESS CHAMBIONS SCHEME (AABCS)
DETAILS
The scheme “Annal Ambedkar Business Champions Scheme (AABCS)” was launched by the Department of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Government of Tamil Nadu. The Government of Tamil Nadu noted that the share of persons from Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe communities who avail of various entrepreneurship promotion subsidies from the Government is very low. In order to promote the economic development of SC/ST entrepreneurs, this scheme has been launched by the Government of Tamil Nadu. The new scheme will provide a 35% capital subsidy and offer a 6% interest subvention for loans to procure machinery and equipment.
This scheme shall be implemented by the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Department through the Industries Commissioner and Director of Industries & Commerce (ICDIC). The Industries Commissioner and Director of Industries and Commerce shall be assisted by FaMeTN, Entrepreneurship Development and Innovation Institute, and StartupTN with manpower and other resources for implementing the Scheme.
A State Level Steering Committee for the scheme shall be constituted with the Secretaries of Finance, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Adi Dravidar and Tribal Welfare Departments, Industries Commissioner and Director of Industries and Commerce, Commissioner of Adi Dravidar Welfare and Commissioner of Tribal Welfare. This Committee will review the scheme once a quarter and suggest necessary modifications, if necessary.
OBJECTIVES
One of the main objective to launching Annal Ambedkar Business Champion Scheme is to provide financial supports to SC/ST Community of the State. Due to this support they can motivate to become entrepreneurs and share economic development of the state. For the successful implementation of the scheme state government allocate 100 Crores INR under the scheme.
NEEDS SCHEME

INTRODUCTION
The scheme “New Entrepreneur-Cum-Enterprise Development Scheme (NEEDS)” was launched by the Department of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Government of Tamil Nadu. The scheme was devised and formulated as a special scheme to assist educated youth to become first-generation entrepreneurs.
OBJECTIVES
- Educated youth will be given entrepreneurship training to groom them as first-generation entrepreneurs on the essentials of conceiving, planning, initiating, and launching a manufacturing or service enterprise successfully.
- On completion of the training program, they would be assisted to prepare their business plans and helped to tie up with financial institutions to get term loans, to set up manufacturing or service enterprises with a project cost not exceeding ₹5 Crore and capital subsidy of 25% of the project cost not exceeding ₹75 lakhs with 3% interest subvention to be provided by the State Government.
- Subject to availability, they would also be provided with reservation up to 25% for allotment of Plots / Sheds in SIDCO Industrial Estates in the State.
PMMY (PRADHAN MANTRI MUDRA YOJANA)
DETAILS
Launched in April 2015 by the Prime Minister, the Mudra Yojana aims to enable Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs), Non-Banking financial institutions/Companies (NBFCs), Small Finance Banks, RBRs, Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks, etc. to provide low interest rate on personal loans to eligible entities.
OBJECTIVES
- Funding the unfunded – To sanction loans up to rupees 10 Lakhs to those who have a business plan to generate income from a non-farm activity like manufacturing, processing, trading, or service sector but don’t have enough capital to invest
- Reducing jobless economic growth – To help generate sources of employment and increase the overall GDP by providing micro-enterprises with credit facilities.
- Monitoring and regulating the Microfinance institutions (MFI) – With the help of MUDRA bank, the network of microfinance institutions will be monitored and new registration will also be done.
- Integration of Informal economy into Formal sector – It will help India also grow its tax base as incomes from the informal sector are non-taxed.
- Promoting financial inclusion – PMMY further adds to the vision of financial inclusion with the aim to reach the last mile credit delivery to micro-businesses and taking the help of technology solutions.
SIDBI LOAN
INTRODUCTION
SIDBI is IDBI’s wholly owned subsidiary, established under a special Act of Parliament in 1988 that went into force on April 2, 1990. SIDBI manages the Small Industries Development Fund and the National Equity Fund, which IDBI formerly managed. It is primarily in charge of encouraging, funding, and advancing middle and small-sized businesses. SIDBI is also involved in the promotion of energy-efficient activities.
OBJECTIVES
- Assist financial institutions on their way to becoming micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in confirming their financial health.
- It makes direct loans to organisations classified in the MSME category.
- It conducts global promotional initiatives for small-scale enterprises.
- It provides bill discounting and rediscounting services.
- It refinances loans to small-scale entities expedited through PLIs and offers resource support to them.
- It offers services such as factoring, leasing, and others to firms operating in the MSME sector.
- It supports employment-oriented industries, particularly in semi-urban regions, to develop work possibilities, preventing people from moving to cities.
- SIDBI also takes measures to modernise and enhance existing businesses technologically.
- SIDBI also co-promotes state-level venture funds.
- It also promotes the timely flow of operating cash and term loans to small businesses.
STAND UP INDIA
INTRODUCTION
Stand-Up India Scheme facilitates bank loans between Rs 10 lakh and Rs 1 Crore to at least one Scheduled Caste (SC) or Scheduled Tribe (ST) borrower and at least one woman borrower per bank branch for setting up a greenfield enterprise. This enterprise may be in manufacturing, services or the trading sector.
OBJECTIVE
The objective of the Stand-Up India scheme is to facilitate bank loans between 10 lakh and 1 Crore to at least one Scheduled Caste (SC) or Scheduled Tribe (ST) borrower and at least one woman borrower per bank branch for setting up a greenfield enterprise. This enterprise may be in manufacturing, services, agri-allied activities or the trading sector In case of non-individual enterprises at least 51% of the shareholding and controlling stake should be held by either an SC/ST or Woman entrepreneur.
CGTMSE LOAN
Introduction
The Board of Trustees of Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE), had framed a Scheme for the purpose of providing guarantees in respect of credit facilities extended by Lending Institutions to the borrowers in Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs). The details of the Scheme are given below:
OBJECTIVE
Availability of bank credit without the hassles of collaterals / third party guarantees would be a major source of support to the first generation entrepreneurs to realise their dream of setting up a unit of their own Micro and Small Enterprise (MSE). Keeping this objective in view, Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME), Government of India launched Credit Guarantee Scheme (CGS) so as to strengthen credit delivery system and facilitate flow of credit to the MSE sector. To operationalise the scheme, Government of India and SIDBI set up the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE).
The lender should cover the eligible credit facilities as soon as they are sanctioned. Guarantee will commence from the date of payment of guarantee fee and shall run through the agreed tenure of the term credit in case of term loans / composite loans and for a period of 5 years where working capital facilities alone are extended to borrowers, or for such period as may be specified by the Guarantee Trust in this behalf.
Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme (CLCSS)
INTRODUCTION
MSMEs in India are often forced to work with obsolete technology due to a shortage of funds. However, this innovative credit scheme functions to help MSMEs located in rural and semi-urban areas improve their existing technology and equipment. CLCSS was introduced by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises to boost production of small scale industries by providing them access to subsidised capital. Under this scheme, eligible enterprises can enjoy a capital subsidy of 15% on loan availed from a financial institution. The primary objectives of this scheme can be described as the intention to upgrade the plant and machinery of enterprises with state-of-art technology, irrespective of expansion. Besides existing MSMEs, new enterprises which have set up as per CLCSS guidelines can qualify as beneficiaries of this scheme.
OBJECTIVES
- The scheme aims at accomplishing the following goals
- To give technology advances through equipment to MSMEs
- To Upgrade MSME’s plant and machinery with the most recent enhancements
- To assist in expansion if needed.
FEATURES OF CLCSS
These are among the most noteworthy characteristics of CLCSS subsidy –
Businesses can receive up to 15% subsidy on their investment in specific machinery under this scheme. It must be noted that the subsidy comes with an upper limit of Rs.1 crore.
CLCSS scheme is available to those enterprises which have put their money in machinery by availing a term loan from the approved list of financial institutions.
Industries that are transitioning from small to medium scale by availing loan under CLCSS are also entitled to benefit from this subsidy scheme.
According to the revised CLSS scheme, an extra 10% subsidy is extended to entrepreneurs who belong to the SC/ST category and hail from the selected districts of the North-East or other hilly terrains.
- 12 nodal agencies oversee Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Schemes. They are –
- Bank of India
- State Bank of India
- Indian bank
- Bank of Baroda
- Andhra Bank
- Punjab National Bank
- Corporation Bank
- Canara Bank
- State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur
- Tamil Nadu Industrial Investment Corporation Limited
- Small Industries Development Bank of India or SIDBI
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development or NABARD
COIR UDYAMI YOJANA (CUY) Schemes
INTRODUCTION
Coir Udyami Yojana is a credit linked subsidy scheme for setting up of coir units with project cost upto Rs.10 lakhs plus one cycle of working capital, which shall not exceed 25% of the project cost. The scheme is being implemented by the Coir Board.
OBJECTIVES
The main objectives of the scheme are as under:
- To modernize Coir Industry by adoption of modern technology in production and processing of coir and coir products;
- Upgradation of the production and processing technology for improving the productivity, quality and product diversification;
- To increase the efficiency and productivity for enhancing the earnings of the workers engaged in the sector;
- To enhance the utilization of coconut husk and fo r increasing the production of coir fibre and coir products;
- To generate employment in the rural areas of the coco nut producing States /Union Territories;
- To provide more employment opportunities for women in the rural sector for gender empowerment;
- To enhance the socio-economic conditions of the producers/workers engaged in the industry;
- To con tribute to inclusive growth of vulnerable sections of beneficiaries especially those belonging to Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST) and North Eastern Region (NER);
- To give sufficient training to the rural youth of the coconut producing States with an eye on attracting them to the fold of coir sector.
To provide backward/forward linkages to the unit holders to whom assistance is given under the Scheme.

